Subcategories:
1 Background and objectives of openIMIS and its governance structure
The openIMIS initiative is focused on creating a sustainable community of practice of various types of users and contributors to the openIMIS software product. In order to achieve and sustain this vibrant openIMIS community, a governance structure to facilitate the various processes within the initiative has been designed. The governance structure aims to define roles and responsibilities to various actors within the community in order to create an efficient and transparent system of information flow and knowledge dissemination. The governance structure aims to bring various stakeholders - current and potential users, implementation and software development experts, specific subject experts onto common platforms to learn about openIMIS, to help develop openIMIS further, or to help spread information about openIMIS further.
The aim of the global openIMIS Initiative is to create a software centred community, where different individuals and organisations at diverse levels are able to contribute to the development and implementation of the openIMIS product. The main objectives of this organisational structure are to:
- Create transparent and efficient governance structures which assign clear roles and responsibilities to the different actors (user countries with their (health) insurers implementing openIMIS, implementation partners, relevant health financing actors, software developers, centralized technical support organisation, technical advisory group, steering group, program coordination desk)
- Offer opportunities for individuals and organisations to learn about openIMIS and become a service provider, e.g. as implementation partner or local support team
- Create an ecosystem which offers
insurancesocial protection?- organisations a range of qualified implementation,
- training and software development/ integration partners to choose from
- Create a stable structure to ensure proper maintenance of existing MS IMIS and to create a user support structure for existing MS IMIS user organisations
- Create a structure for the continuous improvement through addition of new modules and step-by-step transition to a modular open source solution
- Develop a business model where the organisations that use openIMIS contribute to a stable financing of the openIMIS core operations.
- CIF - funding
- Role of the 'initiative' for capacity development?
- capacity development tools availability
- capacity development geared at general awareness building on openIMIS capabilities/functionality etc
- 'on-board' business process (health financing, social protection etc) and ICT experts on openIMIS
- interoperability with other tools in the area - policy side
- 'Grow' openIMIS to be beyond health insurance/financing
- insurance organization → scheme operator
- legacy - modular : transition
- present openimis as a 'solution' to a problem rather than just a 'tool' or software
- security
- performance
- data privacy/ethics
- financing of openimis implementations/country level
- evidence based communication about openIMIS
- growth of the community - local
openIMIS initiative - facilitating the discussion, provides a forum, brings experts to talk about business processes and openIMIS functionality matching; NOT providing the business process solutions.
If direct business process solution design/other scheme design support is required - the initiative recommends service providers.
- show that openimis is the best tool on the market to solve the problems of the customer. evidence!
- independence of evidence?
- encourage 3rd party evaluations ..
2 Roles and responsibilities of parties
A first step towards an organisational structure is the clear definition of roles and responsibilities. For each of the suggested roles we distinguish between ongoing and case driven activities. This distinction serves to separate the more predictable ongoing activities from the case driven activities. The table below visualizes the main partners and their relations.
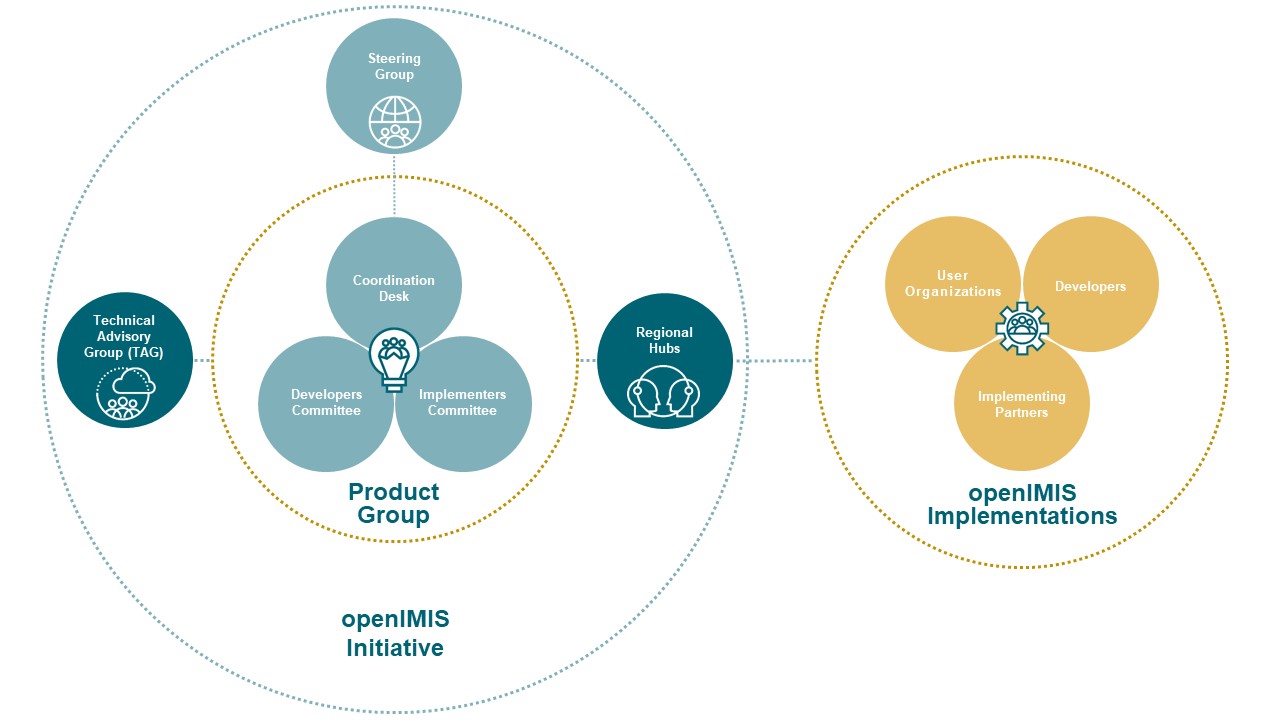
Figure 1: Organisational scheme
The following overview briefly describes the role of each partner:
- Steering Group defines overall strategic direction
- Product Group forms the core group of the openIMIS Initiative.
- It consists of:
- Coordination Desk operationalizes defined strategic direction, administrates budgets and oversees the activities of the involved working groups.
- Developers Committee develops, maintains and supports at global level the core of openIMIS
- Implementers Committee supports at global level implementations regarding implementation steps, training material, requirements of business processes for openIMIS.
- Technical Advisory Group (TAG) assesses the openIMIS Initiative evaluating strategic developments, proposes on system architecture and new functional requirements. The members of the TAG will be nominated by the Steering Group.
- Implementation Consultants facilitates the outreach to the implementations in the countries and builds the link between global and local Community
- Regional hubs provide support to the community on regional level as well as facilitates training and capacity development
- Local support / Dev. Team provides direct support to the payers and providers
- Payers provide feedback on the features of openIMIS and identify future requirements for the system
3 Process flows
In order to clearly define the roles, to avoid overlaps, double work and gaps not covered by any organisation, the main processes of the planned organizational set-up need to be defined in detail, assigning activities to each partner. In this section, a few of the main processes are drafted.
In the column “Who” a main responsible is assigned, sometimes a second organisation is added in brackets to support the process.
3.1 Release Management (Software Maintenance)
One of the main challenges with release management is to coordinate the development of MS IMIS and open source application.
Table 1: Release management workflow
| Who | Activity | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Continuously | ||
| 1.1 | Scheme operators, Implementation Partners | Report issues, request features |
| 1.2 | IT & Product Team |
|
| 1.3 | Steering Group | Annual strategic reviews of features, budgets, timelines |
| 2. At each release cycle | ||
| 2.1 | Program Coordination Desk | Consolidation of user requirements, including interfaces, budget and joint timelines. Preparation of proposal for Product Committee |
| 2.2 | TAG | Receive and process contributions / requirements from partners (JLN, openHIE, clients ...) to the Program Coordination Desk |
| 2.3 | Product Committee |
|
| 2.4 | TAG | When necessary, request input on specific topics from relevant experts. Peer review the technical specifications when necessary |
| 2.5 | IT & Product Team |
|
| 2.6 | Insurance Agencies, Implementation Partners | User acceptance Testing (including security testing?) |
| 2.7 | Product Coordination Desk | Final Acceptance (based on test results and feedback from Insurance Agencies and implementation partners) |
| 2.8 | IT & Product Team |
|
3.2 User support workflow
The main idea is that there is a centralized ticket system (starting at 3rd tier), where users can submit their issues that cannot be solved at country level.
-
Table 2: User support and issue management workflow
| Who | Activity |
|---|---|
| End user / technical user | In case an end-user encounters an issue, he/she reports this to 1st tier support. The local/national team should be able to provide basic support for these issues In case national 1st tier support cannot solve the issue, it is passed on to 2nd tier support. |
| Implementation Partner | Most of the time, implementation partners have support contracts with a local/national project. Therefore, often they can assume 2nd tier support. |
| IT & Product Team | In case the problem cannot be solved at 2nd tier, it should be fed into a central issue queue, and open a ticket at 3rd tier. In this ticket, the submitting 2nd tier support team should describe the issue. |
| IT & Product Team (Program Coordination Desk) | In case the issue can be resolved without much effort, it can be closed. In case the issue requires higher effort, priorities need to be discussed with the Program Coordination Desk / TAG / SG (Process 3.1). |
3.3 Country sales and implementation workflow
There are several possible constellations, how the sales process can unfold. In general, the proposal process should be based on open competition, spreading implementation know-how to a growing number of international, regional and national implementation partners. The IT & Product Team and GIZ should assume the role of supporting the proposal processes of implementation partners upon request.
-
Table 3: Implementation workflow
| Who | Activity |
|---|---|
| Program Coordination Desk | Inform stakeholders about program news and project opportunities |
| TAG | Give feedback on communication and sales strategy, measures and tools |
| Program Coordination Desk | Initial contacts and general information
|
Insurance Agency(potential customer) –Program Coordination Desk (SG) |
|
| Insurer - Implementation partners |
|
| Implementation Partners | Implement software and involve local team |