...
Modularity (and its integration counter-part) is considered at 3 distinct levels:
Solution level, considering the solution as a coherent assembly of Software Components, like Client Registry, Shared Health Record system, Universal Health Coverage,...
Software Component level, where components are decomposed into (activated or not) modules dedicated to fulfil the expected scope for them
Entity level, where each concept hosted by a Software Component can be particularised to the specific needs of an implementation.
Solution level
At Solution level, the roadmap clearly position openIMIS as a component of OpenHIE platform.
The expected modularity at that level is achieved by:
conforming to the OpenHIE platform standards (enforced via the OpenHIE Integration Layer)
adopting the FHIR existing standards to expose openIMIS - managed concepts
Software Component & Entity levels
...
The core platform provides generic components (building blocks) to be used by / particularised in the various plugins and is split in 3 layers:
Frontend(s) layer
Backend layer
Database layer
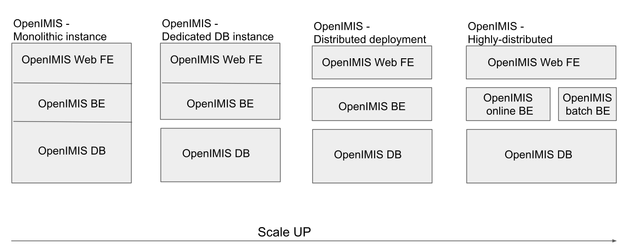
Although openIMIS is an assembly of components (themselves assemblies of plugins), deployments of openIMIS doesn't impose a distributed deployment.
...
Within a project, scaling up by distributing components as the load increases is a very standard (and easy) operation:
...
Further Links
Frontend(s) Target Architecture
Backend (API) Target Architecture
openIMIS is NOT
multi-tenant: while database table will receive a tenant-discriminant (index) column, being multi-tenant requires several precautions we are not going to address in early project phases (like computing/ IO resources sharing, forced coordinated upgrades,...)